What Is Diphtheria? Symptoms, Treatment and Prevention
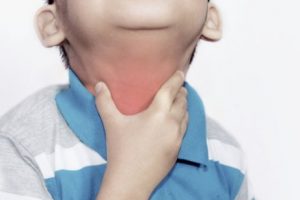
Diphtheria tends to spread in areas where people don’t have the vaccine.
Symptoms of diphtheria
Many people who become infected by diphtheria don’t present strong symptoms. However, in some cases, diphtheria can lead to death.
This illness produces a series of toxins that enter the bloodstream. From there, they travel to the heart, brain and other organs, causing serious organ damage.
These are some of the common symptoms of diphtheria:
- Obstructed airways
- Fever
- Chills
- Sore throat
- Cough
- Snoring
- Difficulty breathing
- Difficulty swallowing
- Wheezing
- The appearance of thick, heavy greyish membranes
- Increased nasal secretion
Complications related to diphtheria
This illness has an incubation period of 2 to 5 days and usually affects a person’s vital organs. Therefore, it’s extremely important to pay attention to the appearance of any symptoms.
Below are the complications that can result if diphtheria is not treated in time:
Damage to the nervous system
When an illness affects the nerves, this can lead to muscular paralysis, which can produce difficulty walking, swallowing and even speaking.
In the worst of cases, individuals with diphtheria who don’t receive medical attention die as a result of the paralysis of the organs that are responsible for breathing.
Damage to the heart
As we mentioned above, this illness produces toxins that enter the bloodstream and affect the vital organs. Among the organs affected by diphtheria is the heart.
Diphtheria can cause inflammation of the cardiac muscle, which can lead to a heart attack. Fatigue and consequent palpitations are signs of damage to the heart by the toxins.
“In some cases, diphtheria can also affect the kidneys”
Treatment of diphtheria
As soon as you suspect the existence of this illness, it’s important to seek immediate treatment. This is true even if diagnosis is not definitive. Treatment of individuals with diphtheria requires hospitalization.
At the same time, isolating the patient is fundamental, given the contagious nature of the disease. In very delicate cases, patients need to stay in intensive care.
Treatment of diphtheria involves the following:
- Antibiotics
Antibiotics are responsible for eliminating the bacteria that are found in the body. This reduces the ability of the disease to continue spreading throughout the body or to other humans as easily. The most common antibiotics used to treat diphtheria are penicillin and erythromycin.
- Antitoxin
Doctors will administer an intravenous or intramuscular antitoxin. In doing so, they neutralize the infection’s advancement through the bloodstream, keeping it from reaching the patient’s organs.
Antitoxins can cause allergic reactions in some individuals, meaning doctors must first do a skin allergy test before administering the substance.
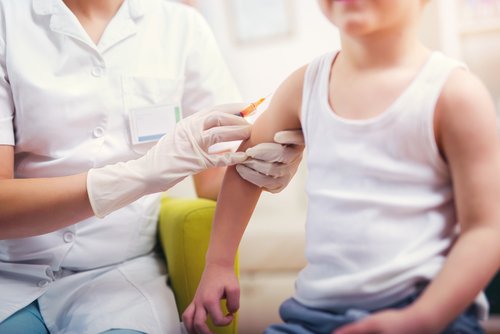
How to prevent diphtheria
The DPT vaccine prevents diphtheria and other serious diseases. It consists of an inactive toxin that doesn’t cause damage to the organs. It produces antibodies that are capable of neutralizing the diphtheria bacteria. The DPT vaccine effectively prevents the appearance of the disease.
In order for the vaccine to work, children must receive 5 doses.
Adults, however, must receive 10 doses of the DPT vaccine in order for it to be effective. Individuals who will be travelling to an area with increased risk for diphtheria should also get an additional dosage. The same is true for people who have been in contact with someone who has the illness.
This extra precaution doesn’t apply to those who have been vaccinated within the past 5 years.

Diphtheria of the skin
This illness can also affect the skin, producing reactions that include redness, pain and swelling. At the same time, it can lead to the appearance of ulcers covered in a greyish membrane.
Just as diphtheria that affects the airways, diphtheria of the skin is also more common in tropical regions. It is more common for people to contract skin diphtheria if they are living in crowded conditions.
Diphtheria is a low risk disease given the existence of a preventative vaccine. Just the same, learning about the illness is important because it spreads easily and is common in tropical areas. Prevention and early detection are key to avoiding complications.
Diphtheria tends to spread in areas where people don’t have the vaccine.
Symptoms of diphtheria
Many people who become infected by diphtheria don’t present strong symptoms. However, in some cases, diphtheria can lead to death.
This illness produces a series of toxins that enter the bloodstream. From there, they travel to the heart, brain and other organs, causing serious organ damage.
These are some of the common symptoms of diphtheria:
- Obstructed airways
- Fever
- Chills
- Sore throat
- Cough
- Snoring
- Difficulty breathing
- Difficulty swallowing
- Wheezing
- The appearance of thick, heavy greyish membranes
- Increased nasal secretion
Complications related to diphtheria
This illness has an incubation period of 2 to 5 days and usually affects a person’s vital organs. Therefore, it’s extremely important to pay attention to the appearance of any symptoms.
Below are the complications that can result if diphtheria is not treated in time:
Damage to the nervous system
When an illness affects the nerves, this can lead to muscular paralysis, which can produce difficulty walking, swallowing and even speaking.
In the worst of cases, individuals with diphtheria who don’t receive medical attention die as a result of the paralysis of the organs that are responsible for breathing.

Damage to the heart
As we mentioned above, this illness produces toxins that enter the bloodstream and affect the vital organs. Among the organs affected by diphtheria is the heart.
Diphtheria can cause inflammation of the cardiac muscle, which can lead to a heart attack. Fatigue and consequent palpitations are signs of damage to the heart by the toxins.
“In some cases, diphtheria can also affect the kidneys”
Treatment of diphtheria
As soon as you suspect the existence of this illness, it’s important to seek immediate treatment. This is true even if diagnosis is not definitive. Treatment of individuals with diphtheria requires hospitalization.
At the same time, isolating the patient is fundamental, given the contagious nature of the disease. In very delicate cases, patients need to stay in intensive care.
Treatment of diphtheria involves the following:
- Antibiotics
Antibiotics are responsible for eliminating the bacteria that are found in the body. This reduces the ability of the disease to continue spreading throughout the body or to other humans as easily. The most common antibiotics used to treat diphtheria are penicillin and erythromycin.
- Antitoxin
Doctors will administer an intravenous or intramuscular antitoxin. In doing so, they neutralize the infection’s advancement through the bloodstream, keeping it from reaching the patient’s organs.
Antitoxins can cause allergic reactions in some individuals, meaning doctors must first do a skin allergy test before administering the substance.
How to prevent diphtheria
The DPT vaccine prevents diphtheria and other serious diseases. It consists of an inactive toxin that doesn’t cause damage to the organs. It produces antibodies that are capable of neutralizing the diphtheria bacteria. The DPT vaccine effectively prevents the appearance of the disease.
In order for the vaccine to work, children must receive 5 doses.
Adults, however, must receive 10 doses of the DPT vaccine in order for it to be effective. Individuals who will be travelling to an area with increased risk for diphtheria should also get an additional dosage. The same is true for people who have been in contact with someone who has the illness.
This extra precaution doesn’t apply to those who have been vaccinated within the past 5 years.

Diphtheria of the skin
This illness can also affect the skin, producing reactions that include redness, pain and swelling. At the same time, it can lead to the appearance of ulcers covered in a greyish membrane.
Just as diphtheria that affects the airways, diphtheria of the skin is also more common in tropical regions. It is more common for people to contract skin diphtheria if they are living in crowded conditions.
Diphtheria is a low risk disease given the existence of a preventative vaccine. Just the same, learning about the illness is important because it spreads easily and is common in tropical areas. Prevention and early detection are key to avoiding complications.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Bush, L. Difteria. Manual MSD (Versión para público general). [En línea].
- Surkis, W; Santoro, J. Vacuna contra el tétanos- difteria. Manual MSD (Versión para público general). [En línea]
- Difteria: preguntas y respuestas en línea. 2017. Organización Mundial de la Salud (OMS). [En línea].
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








