What is Hyperprolactinemia: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment

Hyperprolactinemia occurs when the levels of the prolactin hormone are above normal.
Excessive levels of prolactin can lead to infertility in many cases. This hormonal imbalance can cause menstrual alterations that can make it difficult for a woman to conceive.
The hypophysis, also known as the pituitary gland, is responsible for releasing the prolactin hormone.
This gland has two main functions. First, to intervene in stressful situations. Second, the pituitary gland is responsible for stimulating the production of breast milk during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Causes of hyperprolactinemia
The stimulation of a woman’s nipple during breastfeeding blocks the secretion of a chemical called dopamine. Dopamine is responsible for inhibiting the release of prolactin.
So, when there is a decrease in dopamine, this blocks the inhibition of prolactin. This results in a higher concentration of this hormone in the woman’s blood.
When dopamine levels are low and prolactin levels are high, this is known as negative control. As soon as breastfeeding ceases, the level of prolactin descends.
During pregancy, prolactin increases. This occurs in order to prepare the expectant mother to produce milk. Several hormonal changes occur throughout pregnancy, especially the increase of estrogen. Estrogen also contributes to elevated levels of prolactin.
When prolactin levels are high, the secretion of GnRH – a hormone that releases gonadotropin – stops. The lack of GnRH results in reduced release of the gonadotropins LH (luteinizing hormone) and FWH (follicle-stimulating hormone).
When the action of these hormones upon the ovaries decreases, this impedes ovocitory development and ovulation. Because of this, pregnant women find themselves in a temporary state of infertility caused by hyperprolactinemia.

Other causes of increased prolactin levels
Besides pregnancy and breastfeeding, there are other factors that also contribute to increased levels of prolactin:
- Contraceptives containing estrogen
- A benign tumor, such as prolactinoma
- Orgasm
- High stress levels
- Deep sleep
- Too much physical activity
- Antipsychotics, antidepressants, anxiolytics and some other medications
- Hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism
- Hiperandrogenismo, anorexia nervosa, bulimia, chronic kidney disease, and other conditions
- Stimulation of the breast
Symptoms of hyperlactinemia
There are various symptoms that can be an indication of increased prolactin levels. Not all of the symptoms need to appear in order for hyperlactinemia to be present. Every woman’s experience is different.
Below is a list of the most common symptoms:
- Irregular menstruation or alterations in ovulation
- Headache
- Blurry vision or alteration in a woman’s vision
- Osteoporosis
- Reduced sex drive
- Vaginal dryness
- Infertility
- Galactorrhea
- Weight gain
Bromocriptine and cabergoline reduce prolactin production. These medications work well in most cases of women with prolactinomas.
Diagnosing hyperprolactinemia
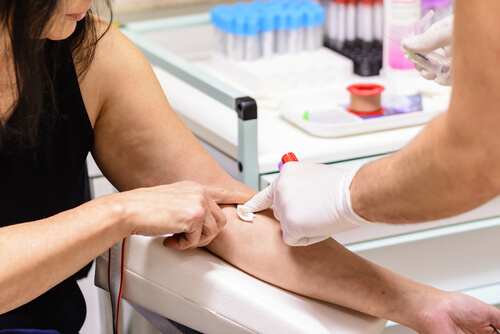
If you believe you may be experiencing hyperprolactinemia, you should talk to your gynecologist. Your doctor will likely order blood tests to determine if your prolactin levels are above normal.
It’s important to have your blood drawn during the morning, after getting a good rest, and avoiding any stressful situation that could increase your prolactin levels.
Normal prolactin levels in women that are not pregnant fall below 25 ng/mL. Your doctor may want you to repeat the testing if your results come back just a bit above normal to determine if you’re suffering from hyperprolactinemia.
High prolactin levels can be alarming, especially when they are above 80-100 ng/mL. This can be an indication of a more serious problem.
It’s also important to find the cause behind hyperprolactinemia. This will involve analyzing the patient’s symptoms, any medications she may be taking, and possible pathologies that could be causing the hyperprolactinemia.
Treating hyperprolactinemia
If the cause of hyperprolactinemia is stress of the administration of a toxic substance, treatment simply involves eliminating the causing factor. When illnesses such as hypothyroidism are to blame, then the treatment will focus on the specific pathology.
Other treatments of hyperprolactinemia involve medications such as bromocriptine and cabergoline. These medications fulfill the function of dopamine, inhibiting the release of prolactin, thus reducing prolactin levels.
Once prolactin levels are normal, this produces the recovery of FSH and LH hormone levels.
If you’re experiencing the symptoms mentioned above, it’s important that you speak to your doctor to detect any irregularity in your health. Remember that you don’t have to have all of the symptoms on the list.
But if you notice that you’re experiencing several of the symptoms, then you may be suffering from hyperprolactinemia.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Bernard V, Young J, Binart N. Prolactin – a pleiotropic factor in health and disease. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019 Jun;15(6):356-365.
- Chaker L, Bianco AC, Jonklaas J, Peeters RP. Hypothyroidism. Lancet. 2017 Sep 23;390(10101):1550-1562.
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








