Ectopic Pregnancy: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment

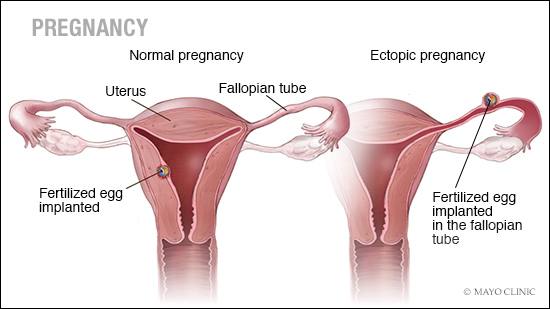
Ectopic pregnancy is one in which the fertilized egg implants itself outside of the uterus. Ectopic, according to the Merrium Webster Dictionary, is something that “occurs in an abnormal position or in an unusual manner or form.” That is precisely what happens in an ectopic pregnancy.
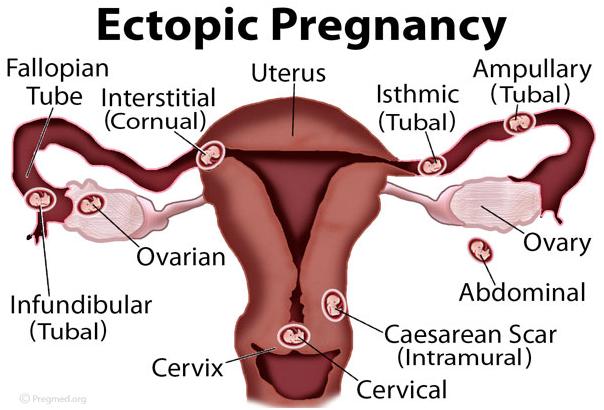
These “abnormal” places where the fertilized egg can be implanted are:
- The fallopian tubes (this is the most common).
- In the union of the fallopian tubes with the uterus.
- One of the ovaries.
- The cervix of your uterus (cervix).
- The abdomen.
Depending on where the egg is implanted, ectopic pregnancy can also have other names. One of these is tubal pregnancy (where the egg settles in the fallopian tubes).
Another is cervical pregnancy (where it implants itself in the neck of the uterus or cervix). It can also be called abdominal pregnancy (when it rests in the abdomen).
None of these places is appropriate for the fetus to develop. First of all, because it doesn’t have enough space to develop, and, secondly, because it doesn’t have the nutritional tissues necessary to feed it.
Causes of ectopic pregnancy
The most frequent reason is damage, inflammation or a narrowing of the fallopian tubes. This makes it more difficult for the egg to move down into the uterus, and it often isn’t able to. This may be due to several factors.
One such factor is a previous operation in the area of the abdomen. Another is having suffered from an infection or condition which has produced an inflammation in the pelvic area. Or, it could also be due to a sexually transmitted infection, such as chlamydia or gonorrhea.
Endometriosis can also be another cause of an ectopic pregnancy. This occurs when the cells that line the inside of the uterus start to grow in other parts of the body.
There are also other factors, such as smoking, having undergone treatments for infertility or even having had another ectopic pregnancy previously.
What are the symptoms and signs of an ectopic pregnancy?
The symptoms that indicate the possible presence of an ectopic pregnancy are:
1. Absence of the menstrual period. You may not notice this absence if the pregnancy occurs at the beginning of the menstrual cycle.
2. Pain or vaginal bleeding. This is another reason why the absence of the period wasn’t noticed.
3. Pain in the pelvis, abdomen and even the shoulders. This may be caused by the irritation of certain nerves, due to the accumulation of blood.
4. Dizziness, nausea or fainting. This is caused by the loss of blood.
5. Hypotension. This is also related to blood loss.
6. Increased frequency of urination. The woman may find she is urinating more than usual.
How is ectopic pregnancy treated?
The treatment can vary, depending on several different factors. One of these is how advanced the pregnancy is. Doctors also take into account what damage there could be in the fallopian tubes, and, logically, the severity of the symptoms. Needless to say, all these factors must be analyzed by a professional doctor.
Sometimes, when the pregnancy is very recent, doctors will inject methotrexate, which causes the embryo to stop growing.
If the pregnancy is more advanced, then surgery to remove the abnormal pregnancy may be necessary. Thanks to today’s technology, and as long as there are no significant organ injuries, this ectopic tissue can be removed by laparoscopy.
This procedure involves the introduction of a video camera and the necessary surgical instruments through a small incision in the lower abdomen.
In this way, the doctor can remove the ectopic tissue and repair, if necessary, the organs damaged by the ectopic pregnancy. In the most serious cases these organs may have to be removed.
There also exists the possibility that the ectopic pregnancy will stop by itself. This often happens when the symptoms aren’t very severe. However, this entails strict monitoring by the professional, with blood tests (to measure the level of HCG in blood) and ultrasound.
Can an ectopic pregnancy be prevented?
No, it isn’t possible to prevent an ectopic pregnancy. It’s something that any woman can suffer from. The possibility, however, is greater in women who are over 35, or who have suffered any of the conditions described above.
What should I do?
You should consult your doctor as soon as possible if any of the previously mentioned symptoms appear. If you have to undergo treatment for an ectopic pregnancy then you should have someone you can share your feelings and experiences with.
If the treatment is successful and there is no serious damage, then the woman can have a perfectly normal pregnancy after having gone through an ectopic pregnancy.
However, this may not be true if you’ve already had fertility problems in the past. Or even if you suspect that you may have an abnormal pregnancy due to the causes already mentioned.
In that case we recommend that you talk with your doctor to find ways to avoid these problems in the future. According to statistics, the chances of a woman suffering repeated ectopic pregnancies is around 15%.
Ectopic pregnancy is one in which the fertilized egg implants itself outside of the uterus. Ectopic, according to the Merrium Webster Dictionary, is something that “occurs in an abnormal position or in an unusual manner or form.” That is precisely what happens in an ectopic pregnancy.
These “abnormal” places where the fertilized egg can be implanted are:
- The fallopian tubes (this is the most common).
- In the union of the fallopian tubes with the uterus.
- One of the ovaries.
- The cervix of your uterus (cervix).
- The abdomen.
Depending on where the egg is implanted, ectopic pregnancy can also have other names. One of these is tubal pregnancy (where the egg settles in the fallopian tubes).
Another is cervical pregnancy (where it implants itself in the neck of the uterus or cervix). It can also be called abdominal pregnancy (when it rests in the abdomen).
None of these places is appropriate for the fetus to develop. First of all, because it doesn’t have enough space to develop, and, secondly, because it doesn’t have the nutritional tissues necessary to feed it.
Causes of ectopic pregnancy
The most frequent reason is damage, inflammation or a narrowing of the fallopian tubes. This makes it more difficult for the egg to move down into the uterus, and it often isn’t able to. This may be due to several factors.
One such factor is a previous operation in the area of the abdomen. Another is having suffered from an infection or condition which has produced an inflammation in the pelvic area. Or, it could also be due to a sexually transmitted infection, such as chlamydia or gonorrhea.

Endometriosis can also be another cause of an ectopic pregnancy. This occurs when the cells that line the inside of the uterus start to grow in other parts of the body.
There are also other factors, such as smoking, having undergone treatments for infertility or even having had another ectopic pregnancy previously.
What are the symptoms and signs of an ectopic pregnancy?
The symptoms that indicate the possible presence of an ectopic pregnancy are:
1. Absence of the menstrual period. You may not notice this absence if the pregnancy occurs at the beginning of the menstrual cycle.
2. Pain or vaginal bleeding. This is another reason why the absence of the period wasn’t noticed.
3. Pain in the pelvis, abdomen and even the shoulders. This may be caused by the irritation of certain nerves, due to the accumulation of blood.
4. Dizziness, nausea or fainting. This is caused by the loss of blood.
5. Hypotension. This is also related to blood loss.
6. Increased frequency of urination. The woman may find she is urinating more than usual.

How is ectopic pregnancy treated?
The treatment can vary, depending on several different factors. One of these is how advanced the pregnancy is. Doctors also take into account what damage there could be in the fallopian tubes, and, logically, the severity of the symptoms. Needless to say, all these factors must be analyzed by a professional doctor.
Sometimes, when the pregnancy is very recent, doctors will inject methotrexate, which causes the embryo to stop growing.
If the pregnancy is more advanced, then surgery to remove the abnormal pregnancy may be necessary. Thanks to today’s technology, and as long as there are no significant organ injuries, this ectopic tissue can be removed by laparoscopy.
This procedure involves the introduction of a video camera and the necessary surgical instruments through a small incision in the lower abdomen.
In this way, the doctor can remove the ectopic tissue and repair, if necessary, the organs damaged by the ectopic pregnancy. In the most serious cases these organs may have to be removed.
There also exists the possibility that the ectopic pregnancy will stop by itself. This often happens when the symptoms aren’t very severe. However, this entails strict monitoring by the professional, with blood tests (to measure the level of HCG in blood) and ultrasound.
Can an ectopic pregnancy be prevented?
No, it isn’t possible to prevent an ectopic pregnancy. It’s something that any woman can suffer from. The possibility, however, is greater in women who are over 35, or who have suffered any of the conditions described above.
What should I do?
You should consult your doctor as soon as possible if any of the previously mentioned symptoms appear. If you have to undergo treatment for an ectopic pregnancy then you should have someone you can share your feelings and experiences with.
If the treatment is successful and there is no serious damage, then the woman can have a perfectly normal pregnancy after having gone through an ectopic pregnancy.
However, this may not be true if you’ve already had fertility problems in the past. Or even if you suspect that you may have an abnormal pregnancy due to the causes already mentioned.
In that case we recommend that you talk with your doctor to find ways to avoid these problems in the future. According to statistics, the chances of a woman suffering repeated ectopic pregnancies is around 15%.
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








