What Are Polyps in the Uterus?

Polyps in the uterus have a much higher incidence in women from 35-40 years old. If you want to know more, read on.
Although the word tumor can scare at first, polyps in the uterus represent a group of tumors that, in their majority, are benign and asymptomatic.
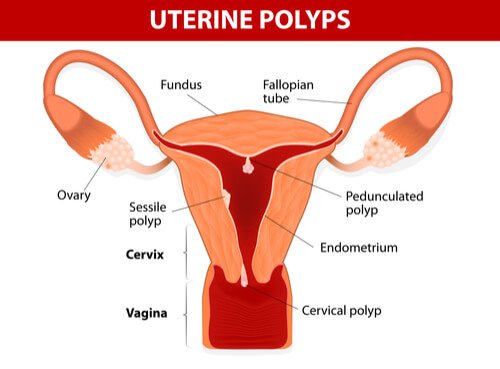
Polyps in the uterus or endometrial polyps are abnormal growths of the layer that lines the uterus, the endometrium. They may have different sizes, although they’re usually small.
In most cases, they don’t cause fertility problems, although in a small percentage they can hinder the arrival of sperm to the ovum.
As they’re usually asymptomatic, there is no sign that tells us they’re there. For that reason, a checkup with your gynecologist is recommended.
Diagnosis of polyps in the uterus
Polyps in the uterus can be found by performing transvaginal ultrasounds, hysterosographs, or hysteroscopies.
- Transvaginal ultrasounds are imaging tests in which an exploration is performed. They introduce a transducer through the vagina, uterus, ovaries and tubes.
- Hysterosographies are a type of ultrasound based on the observation of the endometrium. Physiological saline is used, which helps to distend the uterine cavity. They’re more accurate in diagnosis than transvaginal ultrasounds.
- The most complete tests are the Hysteroscopies, in which a valid diagnosis is achieved. They can also remove the tumor if small and easy to extract. For hysteroscopies, a microscopic camera is used that is introduced through the vagina. A clear image of the polyp or polyps in the uterus is obtained with the camera. Thus, a small piece can be removed to perform a biopsy or remove it whole.
What causes polyps in the uterus?
The specific cause is still unknown. But certain factors are intimately related to the appearance of these tumors. These factors are:
- Increase in estrogen levels.
- Tamoxifen is a drug whose effectiveness has been proven against breast cancer.
- After the age of 40 there is a higher rate of cases of uterine polyps.
- Obesity is associated with multiple complications, including the appearance of polyps.
- Arterial hypertension.
- Hormone treatments in menopausal women.
- Other diseases such as Lynch syndrome or Cowden syndrome – among others – are related to the growth of tumors in the uterus.
Symptoms of polyps in the uterus
They’re usually asymptomatic, so it’s important to perform periodic checkups to rule out their appearance.
Even so, there are polyps that present symptoms. The most common is abnormal uterine bleeding, which is defined as:
- Menorrhagia or menstrual periods with very heavy bleeding.
- Metrorrhagia or bleeding not related to menstruation. This is usually not abundant.
- Bleeding after having sex.
Anemia can be caused by abnormal bleeding, which can be checked through a blood test. If you have one of the situations of abnormal bleeding, don’t hesitate to tell your gynecologist immediately.

Treatment of polyps in the uterus
Let’s keep in mind that each case must be treated specifically. But in general, we can say that removing the polyps is part of the treatment.
Removing the polyps is always recommended for postmenopausal women. In case of perimenopause women, extirpation is recommended in three cases: when they produce symptoms, if they’re too large, or if they’re located in the cervix.
And finally, perimenopause women who don’t present symptoms and whose polyps aren’t multiple should follow their doctor’s medical indications and recommendations for their particular case.
Polyps in the uterus have a much higher incidence in women from 35-40 years old. If you want to know more, read on.
Although the word tumor can scare at first, polyps in the uterus represent a group of tumors that, in their majority, are benign and asymptomatic.
Polyps in the uterus or endometrial polyps are abnormal growths of the layer that lines the uterus, the endometrium. They may have different sizes, although they’re usually small.
In most cases, they don’t cause fertility problems, although in a small percentage they can hinder the arrival of sperm to the ovum.
As they’re usually asymptomatic, there is no sign that tells us they’re there. For that reason, a checkup with your gynecologist is recommended.
Diagnosis of polyps in the uterus
Polyps in the uterus can be found by performing transvaginal ultrasounds, hysterosographs, or hysteroscopies.
- Transvaginal ultrasounds are imaging tests in which an exploration is performed. They introduce a transducer through the vagina, uterus, ovaries and tubes.
- Hysterosographies are a type of ultrasound based on the observation of the endometrium. Physiological saline is used, which helps to distend the uterine cavity. They’re more accurate in diagnosis than transvaginal ultrasounds.
- The most complete tests are the Hysteroscopies, in which a valid diagnosis is achieved. They can also remove the tumor if small and easy to extract. For hysteroscopies, a microscopic camera is used that is introduced through the vagina. A clear image of the polyp or polyps in the uterus is obtained with the camera. Thus, a small piece can be removed to perform a biopsy or remove it whole.

What causes polyps in the uterus?
The specific cause is still unknown. But certain factors are intimately related to the appearance of these tumors. These factors are:
- Increase in estrogen levels.
- Tamoxifen is a drug whose effectiveness has been proven against breast cancer.
- After the age of 40 there is a higher rate of cases of uterine polyps.
- Obesity is associated with multiple complications, including the appearance of polyps.
- Arterial hypertension.
- Hormone treatments in menopausal women.
- Other diseases such as Lynch syndrome or Cowden syndrome – among others – are related to the growth of tumors in the uterus.
Symptoms of polyps in the uterus
They’re usually asymptomatic, so it’s important to perform periodic checkups to rule out their appearance.
Even so, there are polyps that present symptoms. The most common is abnormal uterine bleeding, which is defined as:
- Menorrhagia or menstrual periods with very heavy bleeding.
- Metrorrhagia or bleeding not related to menstruation. This is usually not abundant.
- Bleeding after having sex.
Anemia can be caused by abnormal bleeding, which can be checked through a blood test. If you have one of the situations of abnormal bleeding, don’t hesitate to tell your gynecologist immediately.

Treatment of polyps in the uterus
Let’s keep in mind that each case must be treated specifically. But in general, we can say that removing the polyps is part of the treatment.
Removing the polyps is always recommended for postmenopausal women. In case of perimenopause women, extirpation is recommended in three cases: when they produce symptoms, if they’re too large, or if they’re located in the cervix.
And finally, perimenopause women who don’t present symptoms and whose polyps aren’t multiple should follow their doctor’s medical indications and recommendations for their particular case.
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








