Baby Teeth with Cavities: What's the Best Solution and Why?

Written and verified by the dentist Vanesa Evangelina Buffa
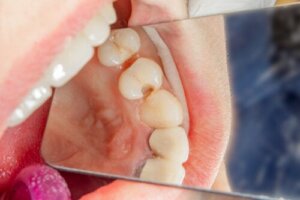
Parents are often faced with the dilemma of whether it’s really necessary to fix their children’s baby teeth with cavities. This question arises because, after a while, they’ll fall out. But the truth is that the restoration of these teeth is always the best option for several reasons. Ideally, children should grow up with all temporary teeth until they fall out naturally.
Although deciduous teeth only remain in the mouth for a short time, they have important functions. Not having these teeth can have negative consequences on your child’s development. In this regard, restoring deciduous teeth when they have cavities allows them to be preserved until they fall out on their own. We’ll explain this in detail in the following article.
The importance of treating baby teeth with cavities
Dental cavities are one of the most frequent diseases worldwide. According to the Global Burden of Disease Study, in 2017, more than 530 million children had cavities in primary teeth. A 2018 report from the American Academy of Pediatric Dentists revealed that 18% of children aged 2 to 5 years, in the United States, had cavities. This figure increased to 45% between the ages of 6 and 11. In addition, 15% of these lesions didn’t receive the corresponding dental treatment.
When dental cavities aren’t treated, they can cause pain, infections, difficulty chewing, and nutritional problems. In addition, children with this disease often experience self-esteem problems and difficulties at school due to the associated discomfort.
It’s true that baby teeth remain in children’s mouths for a limited period of time, but this’s no reason to neglect them. Nor is it a reason to extract them prematurely. Temporary teeth perform specific tasks and their early loss deprives little ones of many of these important functions for their growth and for the normal development of their daily life.
Let’s see in detail the main functions of baby teeth and why they should be fixed if they have cavities.

Chewing
Chewing is a very important function in everyone’s life, as our correct nutrition depends on it. The appearance of temporary teeth in the mouths of babies helps them learn to chew. As the child grows, they can use this skill to make their diet more complex and incorporate all kinds of foods.
If baby teeth with cavities aren’t treated in a timely manner, they can break, be lost, or need to be extracted. In addition, not treating them can be associated with nutritional problems in children.
Speech
Baby teeth are also involved in speech development. Many phonemes require the presence of the teeth to sound correctly. The “f” or “s” sounds, for example, need to be supported by the teeth in order to be produced. Therefore, if they’re not fixed or are lost or removed, the pronunciation of some words can be compromised. This can lead to school problems, communication difficulties, teasing, embarrassment, and a lack of self-esteem.
Development of the jaws and guidance of the definitive eruption
Baby teeth in their proper position favor the growth and development of the jaws. These teeth reserve the space needed for the permanent teeth to erupt and position themselves correctly in the arch. In addition, not fixing baby teeth or removing them prematurely can lead to bite problems. By removing the primary teeth prematurely, the other elements of the mouth are mobilized to close the gap.
Also, impacted teeth, crooked or crowded teeth, and other occlusion problems are associated with the premature loss of baby teeth. If these bite alterations appear, orthodontic treatment will be necessary to correct them.
Aesthetics
Aesthetics is another function of baby teeth that’s sometimes overlooked by adults. Having all teeth healthy improves a child’s appearance. It may not seem like this role is very important, but having a neat smile prevents teasing from other children and improves self-esteem and self-confidence.
The complications of not fixing baby teeth with cavities
Not treating baby teeth with cavities in a timely manner can lead to certain complications:
- Pain: Teeth with cavities can cause sensitivity or pain when chewing or upon contact with cold, hot, or sweet foods. Sharp, throbbing pain in the mouth disrupts the child’s daily activities, as they can’t eat, play, learn, or rest normally.
- Infections: Abscesses in the root zone can complicate the development of the definitive elements that form in the thickness of the bone. In addition, they can spread to other parts of the body and compromise the overall health of the child.
- More cavities: Not treating cavities in baby teeth generates oral conditions that favor the disease to continue and develop in the other dental elements. In children with mixed dentition, there’s a risk of the pathology occurring in the newly erupted permanent teeth.

Fixing baby teeth with cavities
When it comes to fixing baby teeth with cavities, there are different procedures depending on the needs of the particular clinical case. When the cavities have just started, enamel remineralization treatments can be used. On the other hand, if the lesions are larger and there’s more loss of dental tissue, fillings or crowns will be necessary. In addition, if the cavity has caused damage, it’s necessary to resort to endodontics for children.
Only in cases where treatment isn’t possible or the damage to the tooth poses a greater risk to the child, dental extractions are used.
When not to treat baby teeth with cavities?
One reason for not treating a baby tooth with cavities is because the tooth moves and is close to coming out. Only in this case can the pediatric dentist avoid treatment and wait for the tooth to fall out or extract it to avoid complications. In any case, if the specialist decides not to treat the element, it’s important to be aware of the possible complications. It will always be the professional who makes the decision and monitors the evolution of the case.
The dentist’s criteria
When deciding what’s best for each child, it’ll be the evaluation of the particularities and needs of each case that will lead the pediatric dentist to choose the best treatment. The best option is to treat them as soon as possible to avoid further damage. Otherwise, letting the disease progress causes problems in many aspects of the child’s life. Only if the piece moves and is about to fall out, the professional may suggest waiting for dental replacement without treatment.
It’s important that parents take their children to biannual dental checkups to detect any damage to the teeth early on. Early diagnosis avoids inconvenience and discomfort in children and the need for more complex and costly treatments in the future.
Parents are often faced with the dilemma of whether it’s really necessary to fix their children’s baby teeth with cavities. This question arises because, after a while, they’ll fall out. But the truth is that the restoration of these teeth is always the best option for several reasons. Ideally, children should grow up with all temporary teeth until they fall out naturally.
Although deciduous teeth only remain in the mouth for a short time, they have important functions. Not having these teeth can have negative consequences on your child’s development. In this regard, restoring deciduous teeth when they have cavities allows them to be preserved until they fall out on their own. We’ll explain this in detail in the following article.
The importance of treating baby teeth with cavities
Dental cavities are one of the most frequent diseases worldwide. According to the Global Burden of Disease Study, in 2017, more than 530 million children had cavities in primary teeth. A 2018 report from the American Academy of Pediatric Dentists revealed that 18% of children aged 2 to 5 years, in the United States, had cavities. This figure increased to 45% between the ages of 6 and 11. In addition, 15% of these lesions didn’t receive the corresponding dental treatment.
When dental cavities aren’t treated, they can cause pain, infections, difficulty chewing, and nutritional problems. In addition, children with this disease often experience self-esteem problems and difficulties at school due to the associated discomfort.
It’s true that baby teeth remain in children’s mouths for a limited period of time, but this’s no reason to neglect them. Nor is it a reason to extract them prematurely. Temporary teeth perform specific tasks and their early loss deprives little ones of many of these important functions for their growth and for the normal development of their daily life.
Let’s see in detail the main functions of baby teeth and why they should be fixed if they have cavities.

Chewing
Chewing is a very important function in everyone’s life, as our correct nutrition depends on it. The appearance of temporary teeth in the mouths of babies helps them learn to chew. As the child grows, they can use this skill to make their diet more complex and incorporate all kinds of foods.
If baby teeth with cavities aren’t treated in a timely manner, they can break, be lost, or need to be extracted. In addition, not treating them can be associated with nutritional problems in children.
Speech
Baby teeth are also involved in speech development. Many phonemes require the presence of the teeth to sound correctly. The “f” or “s” sounds, for example, need to be supported by the teeth in order to be produced. Therefore, if they’re not fixed or are lost or removed, the pronunciation of some words can be compromised. This can lead to school problems, communication difficulties, teasing, embarrassment, and a lack of self-esteem.
Development of the jaws and guidance of the definitive eruption
Baby teeth in their proper position favor the growth and development of the jaws. These teeth reserve the space needed for the permanent teeth to erupt and position themselves correctly in the arch. In addition, not fixing baby teeth or removing them prematurely can lead to bite problems. By removing the primary teeth prematurely, the other elements of the mouth are mobilized to close the gap.
Also, impacted teeth, crooked or crowded teeth, and other occlusion problems are associated with the premature loss of baby teeth. If these bite alterations appear, orthodontic treatment will be necessary to correct them.
Aesthetics
Aesthetics is another function of baby teeth that’s sometimes overlooked by adults. Having all teeth healthy improves a child’s appearance. It may not seem like this role is very important, but having a neat smile prevents teasing from other children and improves self-esteem and self-confidence.
The complications of not fixing baby teeth with cavities
Not treating baby teeth with cavities in a timely manner can lead to certain complications:
- Pain: Teeth with cavities can cause sensitivity or pain when chewing or upon contact with cold, hot, or sweet foods. Sharp, throbbing pain in the mouth disrupts the child’s daily activities, as they can’t eat, play, learn, or rest normally.
- Infections: Abscesses in the root zone can complicate the development of the definitive elements that form in the thickness of the bone. In addition, they can spread to other parts of the body and compromise the overall health of the child.
- More cavities: Not treating cavities in baby teeth generates oral conditions that favor the disease to continue and develop in the other dental elements. In children with mixed dentition, there’s a risk of the pathology occurring in the newly erupted permanent teeth.

Fixing baby teeth with cavities
When it comes to fixing baby teeth with cavities, there are different procedures depending on the needs of the particular clinical case. When the cavities have just started, enamel remineralization treatments can be used. On the other hand, if the lesions are larger and there’s more loss of dental tissue, fillings or crowns will be necessary. In addition, if the cavity has caused damage, it’s necessary to resort to endodontics for children.
Only in cases where treatment isn’t possible or the damage to the tooth poses a greater risk to the child, dental extractions are used.
When not to treat baby teeth with cavities?
One reason for not treating a baby tooth with cavities is because the tooth moves and is close to coming out. Only in this case can the pediatric dentist avoid treatment and wait for the tooth to fall out or extract it to avoid complications. In any case, if the specialist decides not to treat the element, it’s important to be aware of the possible complications. It will always be the professional who makes the decision and monitors the evolution of the case.
The dentist’s criteria
When deciding what’s best for each child, it’ll be the evaluation of the particularities and needs of each case that will lead the pediatric dentist to choose the best treatment. The best option is to treat them as soon as possible to avoid further damage. Otherwise, letting the disease progress causes problems in many aspects of the child’s life. Only if the piece moves and is about to fall out, the professional may suggest waiting for dental replacement without treatment.
It’s important that parents take their children to biannual dental checkups to detect any damage to the teeth early on. Early diagnosis avoids inconvenience and discomfort in children and the need for more complex and costly treatments in the future.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- AAPD Pediatric Oral Health Research and Policy Center. (2018). Snapshot of America’s children 2018. Available at: https://www.aapd.org/assets/1/7/Childs_Snapshot_2018_web_version.pdf
- Achmad, H., Ramadany, S., Sukmana, B. I., Hanan, N., Hartami, E., Mutmainnah, N., … & Pagala, M. I. (2020). A review of stunting growth in children: relationship to the incidence of dental caries and its handling in children. Systematic Reviews in Pharmacy, 11(6), 230-235.
- Cubero Santos, A., Lorido Cano, I., González Huéscar, A., Ferrer García, M., Zapata Carrasco, M., & Ambel Sánchez, J. L. (2019). Prevalencia de caries dental en escolares de educación infantil de una zona de salud con nivel socioeconómico bajo. Pediatría Atención Primaria, 21(82), e47-e59.
- Finucane, D. (2019). Restorative treatment of primary teeth: an evidence‐based narrative review. Australian Dental Journal, 64, S22-S36.
- Jackson, S. L., Vann Jr, W. F., Kotch, J. B., Pahel, B. T., & Lee, J. Y. (2011). Impact of poor oral health on children’s school attendance and performance. American journal of public health, 101(10), 1900-1906.
- Karki, S., Päkkilä, J., Ryhänen, T., Laitala, M. L., Humagain, M., Ojaniemi, M., & Anttonen, V. (2019). Body mass index and dental caries experience in Nepalese schoolchildren. Community dentistry and oral epidemiology, 47(4), 346-357.
- Organización Mundial de la Salud. (2021). Poner fin a la caries dental en la infancia: manual de aplicación de la OMS. Organización Mundial de la Salud. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/340445. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO
- Seirawan, H., Faust, S., & Mulligan, R. (2012). The impact of oral health on the academic performance of disadvantaged children. American journal of public health, 102(9), 1729-1734.
- Tickle, M., Milsom, K., & Kennedy, A. (1999). Is it better to leave or restore carious deciduous molar teeth? A preliminary study. Primary Dental Care: Journal of the Faculty of General Dental Practitioners (UK), 6(4), 127-131.
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








