Is Coronavirus Dangerous for Children?

Coronavirus is the epidemic that everyone is talking about around the world. This is due to how fast it spreads from one person to the next. But what about our little ones? Is coronavirus dangerous for children? Should we sound the alarms?
What is coronavirus?
Coronaviruses are a family of viruses with an unknown origin, and there are different types of coronavirus. They can produce symptoms that vary from coughing to pneumonia. In the most serious cases, it can cause respiratory failure.
In December 2019, the first cases of a new type of coronavirus – COVID-19 – were detected in the city of Wuhan in China. Since then, the spread from one infected individual to another healthy individual has caused the number of cases to increase drastically.
Though the number of people that have caught the coronavirus is very high, the mortality rate of this type of virus is actually low. In fact, it’s even lower than previous epidemics of other types of coronavirus.
You may also want to read: What Is the Influenza Virus
What symptoms does the virus produce?
A coronavirus infection, in general, produces symptoms that are similar to those of the common flu. Among them, we can find the following:
- Nasal dripping
- Overall discomfort
- Tiredness
- Muscular pain
- Coughing
- Runny nose
- Fever and the chills
- Sore throat and headache
A person carrying the infection may remain without symptoms, experience flu-like symptoms like the above, or come to suffer more serious complications. The most important complications can vary from pneumonia to respiratory failure.
These more serious cases, in general, occur among more vulnerable populations. These include the elderly, newborn babies, and those with a suppressed immune system.
Is coronavirus dangerous for children?
It seems that coronavirus infection is, in general, much milder in the case of children. And, as we’ve said, the mortality rate related to this strain of the virus is low. Therefore, different organisms have sent out reassuring messages regarding coronavirus and children.
Nevertheless, the American Academy of Pediatrics, together with other pediatric institutions, aims to prepare a protocol regarding how to respond to and manage coronavirus in children.
Of course, being on alert is paramount. Those who suspect any possible case of the virus should alert public health officials without delay. That way, they can put appropriate measures into place in order to confirm or rule out infection.
How to prevent and treat coronavirus
Currently, no effective treatment of coronavirus exists. Rather, medical professionals focus on treating symptoms, controlling fever and pain, and trying to maintain patients’ overall health.
It’s also important to be on alert regarding the appearance of possible complications. This is especially important, as we’ve said, in regard to the most susceptible populations.
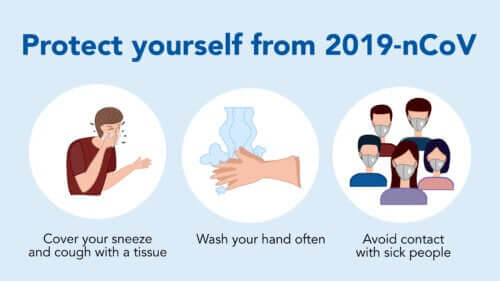
This is why it’s so important to avoid the spread of coronavirus from one person to another. Therefore, the best means of prevention is practicing proper hygiene. In other words, basic overall hygiene. What’s more, individuals should place extra importance on hygiene involving their hands.
It’s also very important to avoid contact with those who already have the virus. If this contact can’t be avoided, then you should cover your eyes, mouth, and nose.
You may also want to read: Are Antibiotics Effective Against All Viruses?
Conclusion: Is coronavirus dangerous for children?
While alarms regarding this virus area already going off around the globe, experts are advising people to stay calm. In regard to the question – “Is coronavirus dangerous for children?” – the answer is generally no. The virus doesn’t seem to be especially aggressive among children.
What’s more, the rapid action on behalf of health officials makes it possible to control and even reduce the spread of coronavirus. Just the same, if you have any doubts or suspect a case of coronavirus, consult a medical specialist right away.
Coronavirus is the epidemic that everyone is talking about around the world. This is due to how fast it spreads from one person to the next. But what about our little ones? Is coronavirus dangerous for children? Should we sound the alarms?
What is coronavirus?
Coronaviruses are a family of viruses with an unknown origin, and there are different types of coronavirus. They can produce symptoms that vary from coughing to pneumonia. In the most serious cases, it can cause respiratory failure.
In December 2019, the first cases of a new type of coronavirus – COVID-19 – were detected in the city of Wuhan in China. Since then, the spread from one infected individual to another healthy individual has caused the number of cases to increase drastically.

Though the number of people that have caught the coronavirus is very high, the mortality rate of this type of virus is actually low. In fact, it’s even lower than previous epidemics of other types of coronavirus.
You may also want to read: What Is the Influenza Virus
What symptoms does the virus produce?
A coronavirus infection, in general, produces symptoms that are similar to those of the common flu. Among them, we can find the following:
- Nasal dripping
- Overall discomfort
- Tiredness
- Muscular pain
- Coughing
- Runny nose
- Fever and the chills
- Sore throat and headache
A person carrying the infection may remain without symptoms, experience flu-like symptoms like the above, or come to suffer more serious complications. The most important complications can vary from pneumonia to respiratory failure.
These more serious cases, in general, occur among more vulnerable populations. These include the elderly, newborn babies, and those with a suppressed immune system.
Is coronavirus dangerous for children?
It seems that coronavirus infection is, in general, much milder in the case of children. And, as we’ve said, the mortality rate related to this strain of the virus is low. Therefore, different organisms have sent out reassuring messages regarding coronavirus and children.
Nevertheless, the American Academy of Pediatrics, together with other pediatric institutions, aims to prepare a protocol regarding how to respond to and manage coronavirus in children.
Of course, being on alert is paramount. Those who suspect any possible case of the virus should alert public health officials without delay. That way, they can put appropriate measures into place in order to confirm or rule out infection.
How to prevent and treat coronavirus
Currently, no effective treatment of coronavirus exists. Rather, medical professionals focus on treating symptoms, controlling fever and pain, and trying to maintain patients’ overall health.

It’s also important to be on alert regarding the appearance of possible complications. This is especially important, as we’ve said, in regard to the most susceptible populations.
This is why it’s so important to avoid the spread of coronavirus from one person to another. Therefore, the best means of prevention is practicing proper hygiene. In other words, basic overall hygiene. What’s more, individuals should place extra importance on hygiene involving their hands.
It’s also very important to avoid contact with those who already have the virus. If this contact can’t be avoided, then you should cover your eyes, mouth, and nose.
You may also want to read: Are Antibiotics Effective Against All Viruses?
Conclusion: Is coronavirus dangerous for children?
While alarms regarding this virus area already going off around the globe, experts are advising people to stay calm. In regard to the question – “Is coronavirus dangerous for children?” – the answer is generally no. The virus doesn’t seem to be especially aggressive among children.
What’s more, the rapid action on behalf of health officials makes it possible to control and even reduce the spread of coronavirus. Just the same, if you have any doubts or suspect a case of coronavirus, consult a medical specialist right away.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Calendario de vacunaciones de la Asociación Española de Pediatría: Recomendaciones 2011* [Vacunas (Madr).2011]-Medes [Internet]. [cited 2020 Feb 19]. Available from: https://medes.com/publication/67076
- Coelho M, Arruda CS, Simões SF. HIGIENIZAÇÃO DAS MÃOS COMO ESTRATÉGIA FUNDAMENTAL NO CONTROLE DE INFECÇÃO HOSPITALAR: UM ESTUDO QUANTITATIVO. Enfermería Glob. 2011 Jan 16;10(21).
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








