10 Common Causes of Rashes in Children

Written and verified by the dermatologist Maria del Carmen Hernandez
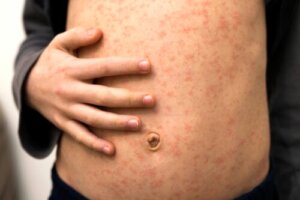
Rashes in children are a common condition that can be caused for a variety of reasons. In turn, some of them are usually contagious, however, they’re not serious. Just the same, they cause discomfort and embarrassment to sufferers due to their obvious clinical manifestations.
Causes of rashes in children
The causes of rashes in children are different, however, some of them may have similar signs and symptoms.
Atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic, relapsing, and very itchy skin disease. It develops due to alteration of the skin barrier in genetically predisposed children’s skin.
Atopic disease is associated with poor school performance, family dysfunction, and low self-esteem according to publications in the Archives of Disease in Childhood. Xerosis and pruritus are the main symptoms, and the rashes occur on the face, scalp, and extensor regions in infants and young children.

Contact dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is a common disease in the pediatric age group. It’s further classified into allergic and irritant forms. It’s triggered by direct contact with substances that are allergens for the body.
It often causes lesions only in the area of contact, but there are cases in which the lesions can be located at a distance from the original contact site. Some of the most common allergens are perfumes, nickel, costume jewelry, and cosmetics.
Pityriasis versicolor, one of the causes of rashes in children
Also known as tinea versicolor, it’s characterized as an infection of the superficial layer of the skin. It’s benign and frequent.
The Malassezia fungus generates macules that present fine scales with different shades of pigmentation. The most affected areas are the trunk, back, and shoulders.
It’s usually treated effectively and quickly with topical antifungal agents. In turn, it’s a disease that isn’t contagious, but it can generate embarrassment and discomfort in those affected.
Insect bites
Insects can cause itching and pain in the area where they bite. In some children, it can even trigger a severe allergic response called anaphylaxis.
Some of the most predisposing insects are wasps, ticks, mosquitoes, bees, or fire ants. Milder manifestations can range from hives to intense itching.
Certain bites can develop specific diseases, such as Lyme disease, Zika Virus, or Rocky Mountain spotted fever.
You may be interested in: Guide to Identifying Insect Bites in Children
Seborrheic dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is an inflammatory skin disease that presents with a papulosquamous morphology in areas where there are a large number of sebaceous glands.
The areas of greatest involvement are the scalp, body folds, and face. In addition, the lesions don’t usually cause itching or pain, but discomfort or embarrassment about cosmetic appearance.
Impetigo, another cause of rashes in children
Impetigo is one of the most common skin infections in childhood. It’s caused by gram-negative bacteria and is highly contagious. It’s characterized by the presence of erythematous plaques with yellow crusts on their surface that cause pain or itching.
Treatment consists of the application of antibiotic creams on a daily basis. This therapy is effective in 90% of cases.
Gilbert’s pityriasis rosea
Gilbert’s pityriasis rosea is an acute papulosquamous disease. It’s characterized by an initial scaly plaque, larger than those of later onset.
These scaly plaques are distributed on the back, trunk, and proximal extremities. In fact, reference is often made to the Christmas tree distribution of the lesions.
It’s a disease that resolves spontaneously, although in some cases, antihistamine medication should be prescribed due to intense itching.
Read also: Scabies in Children: Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
Molluscum contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is a benign skin condition characterized by a high degree of contagiousness. The typical lesion is dome-shaped, round, and pinkish-purple in color. Transmission takes place through direct contact with these lesions.
They usually resolve on their own, but attempts are made to accelerate the process with topical treatment or curettage to prevent the spread of the lesions.

Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic, inflammatory skin condition that can occur in children or adults. However, lesions in children may vary in their distribution and morphology.
The diagnosis is based on the clinical manifestations of the lesions, which in children are usually erythematous plaques of thinner and smaller white scales.
10. Scabies
Scabies is an infectious disease caused by a highly contagious mite. The mite hides inside the skin and causes papular lesions and intense itching, predominantly at night. The areas of the body most affected are the areolas, interdigital folds, wrists, and periumbilical area.
What to do about rashes in children?
Each type of rash has a cause that triggers it. For this reason, it’s important not to self-medicate and, at the first sight of symptomatology, go to a specialist. The doctor will be the one who, according to the factor that provoked it, will indicate the treatment or the necessary measures to manage it.
Rashes in children are a common condition that can be caused for a variety of reasons. In turn, some of them are usually contagious, however, they’re not serious. Just the same, they cause discomfort and embarrassment to sufferers due to their obvious clinical manifestations.
Causes of rashes in children
The causes of rashes in children are different, however, some of them may have similar signs and symptoms.
Atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic, relapsing, and very itchy skin disease. It develops due to alteration of the skin barrier in genetically predisposed children’s skin.
Atopic disease is associated with poor school performance, family dysfunction, and low self-esteem according to publications in the Archives of Disease in Childhood. Xerosis and pruritus are the main symptoms, and the rashes occur on the face, scalp, and extensor regions in infants and young children.

Contact dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is a common disease in the pediatric age group. It’s further classified into allergic and irritant forms. It’s triggered by direct contact with substances that are allergens for the body.
It often causes lesions only in the area of contact, but there are cases in which the lesions can be located at a distance from the original contact site. Some of the most common allergens are perfumes, nickel, costume jewelry, and cosmetics.
Pityriasis versicolor, one of the causes of rashes in children
Also known as tinea versicolor, it’s characterized as an infection of the superficial layer of the skin. It’s benign and frequent.
The Malassezia fungus generates macules that present fine scales with different shades of pigmentation. The most affected areas are the trunk, back, and shoulders.
It’s usually treated effectively and quickly with topical antifungal agents. In turn, it’s a disease that isn’t contagious, but it can generate embarrassment and discomfort in those affected.
Insect bites
Insects can cause itching and pain in the area where they bite. In some children, it can even trigger a severe allergic response called anaphylaxis.
Some of the most predisposing insects are wasps, ticks, mosquitoes, bees, or fire ants. Milder manifestations can range from hives to intense itching.
Certain bites can develop specific diseases, such as Lyme disease, Zika Virus, or Rocky Mountain spotted fever.
You may be interested in: Guide to Identifying Insect Bites in Children
Seborrheic dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is an inflammatory skin disease that presents with a papulosquamous morphology in areas where there are a large number of sebaceous glands.
The areas of greatest involvement are the scalp, body folds, and face. In addition, the lesions don’t usually cause itching or pain, but discomfort or embarrassment about cosmetic appearance.
Impetigo, another cause of rashes in children
Impetigo is one of the most common skin infections in childhood. It’s caused by gram-negative bacteria and is highly contagious. It’s characterized by the presence of erythematous plaques with yellow crusts on their surface that cause pain or itching.
Treatment consists of the application of antibiotic creams on a daily basis. This therapy is effective in 90% of cases.
Gilbert’s pityriasis rosea
Gilbert’s pityriasis rosea is an acute papulosquamous disease. It’s characterized by an initial scaly plaque, larger than those of later onset.
These scaly plaques are distributed on the back, trunk, and proximal extremities. In fact, reference is often made to the Christmas tree distribution of the lesions.
It’s a disease that resolves spontaneously, although in some cases, antihistamine medication should be prescribed due to intense itching.
Read also: Scabies in Children: Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
Molluscum contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is a benign skin condition characterized by a high degree of contagiousness. The typical lesion is dome-shaped, round, and pinkish-purple in color. Transmission takes place through direct contact with these lesions.
They usually resolve on their own, but attempts are made to accelerate the process with topical treatment or curettage to prevent the spread of the lesions.

Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic, inflammatory skin condition that can occur in children or adults. However, lesions in children may vary in their distribution and morphology.
The diagnosis is based on the clinical manifestations of the lesions, which in children are usually erythematous plaques of thinner and smaller white scales.
10. Scabies
Scabies is an infectious disease caused by a highly contagious mite. The mite hides inside the skin and causes papular lesions and intense itching, predominantly at night. The areas of the body most affected are the areolas, interdigital folds, wrists, and periumbilical area.
What to do about rashes in children?
Each type of rash has a cause that triggers it. For this reason, it’s important not to self-medicate and, at the first sight of symptomatology, go to a specialist. The doctor will be the one who, according to the factor that provoked it, will indicate the treatment or the necessary measures to manage it.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Su JC, Kemp AS, Varigos GA, Nolan TM. (1997). Atopic eczema: its impact on the family and financial cost. Arch Dis Child. 1997 Feb;76(2):159-62. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9068310/
- Prohic A, Jovovic Sadikovic T, Krupalija-Fazlic M, Kuskunovic-Vlahovljak S. (2016). Malassezia species in healthy skin and in dermatological conditions. Int J Dermatol. 2016 May;55(5):494-504. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26710919/
- Darmstadt GL, Lane AT. (1994). Impetigo: an overview. Pediatr Dermatol. 1994 Dec;11(4):293-303. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7899177/
- Drago F, Ciccarese G, Parodi A. (2018). Pityriasis rosea and pityriasis rosea-like eruptions: How to distinguish them? JAAD Case Rep. 2018 Sep 14;4(8):800-801. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30246131/
- Müller CSL, Laue M, Kremer K, Becker S, Vogt T, Smola S. Molluscum-contagiosum-Virus in einer Epidermalzyste. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2018 Sep;16(9):1144-1146. doi: 10.1111/ddg.13633_g. PMID: 30179331.
- Seyhan M, Coşkun BK, Sağlam H, Ozcan H, Karincaoğlu Y. Psoriasis in childhood and adolescence: evaluation of demographic and clinical features. Pediatr Int. 2006 Dec;48(6):525-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-200X.2006.02270.x. PMID: 17168968.
- Clínica Mayo. (2022). Erupción por hiedra venenosa. Consultado el 12 de febrero de 2023. https://www.mayoclinic.org/es-es/diseases-conditions/poison-ivy/symptoms-causes/syc-20376485.
- Clínica Mayo. (2022). Dermatitis de contacto. Consultado el 12 de febrero de 2023. https://www.mayoclinic.org/es-es/diseases-conditions/contact-dermatitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20352742.
- Clínica Mayo. (2022). Dermatitis seborreica. Consultado el 12 de febrero de 2023. https://www.mayoclinic.org/es-es/diseases-conditions/seborrheic-dermatitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20352710.
- Comunidad Autónoma de Madrid. (S.F.) Escabiosis. Consultado el 12 de febrero de 2023. https://www.comunidad.madrid/servicios/salud/escabiosis.
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








