Digestive Illnesses in Children: What You Should Know

Digestive illnesses in children can affect any organ that makes up the digestive system. The food we eat must undergo a transformation process before becoming molecules that the cells can use. These changes begin in the mouth with chewing and continue in the esophagus and the stomach, where gastric juices break foods down into smaller particles.
The small intestine, specifically the intestinal villi, is the organ of the digestive system where the absorption of nutrients takes place. Finally, digestion ends in the large intestine and the anus with the elimination of those products that we discard.
Other glands such as the pancreas and the gallbladder or organs such as the liver also participate in this process by producing juices that help in the transformation of nutrients. Any alteration during the process makes digestion difficult and, in some cases, lead to digestive illnesses in children.
Mild digestive illnesses in children
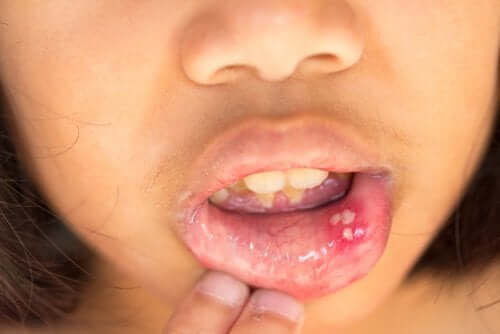
Herpetic gingivostomatitis
Herpes simplex virus is a contagious disease caused by infection with herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1). In fact, that’s its primary manifestation. When it comes to adults, it appears in the form of typical herpes in the lip area. However, in children, it causes very painful ulcerous lesions inside the mouth and on the surface of the tongue.
Reflux in newborns
Gastroesophageal reflux occurs when some of the stomach contents back up into the esophagus if the esophageal sphincter doesn’t close properly. In infants, this continued reflux accompanied by vomiting can cause irritation of the area, weight loss, and, on rare occasions, breathing problems.
Infectious gastroenteritis
This contagious disease is caused by eating contaminated food or sucking on an item of an ill child. It’s a very common illness in daycare centers that involves abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, nausea, and fever. It’s usually caused by a 24-hour transient virus (rotavirus).
Moderate digestive illnesses in children
Celiac disease
Celiac disease is a digestive disorder with a marked genetic component that affects the intestinal villi of the small intestine produced by the intake of gluten. In the most extreme cases, children may suffer from severe malnutrition, reflected by growth retardation, rickets, and even mood swings. As for treatment, it involves removing gluten completely from the child’s diet.
Lactose intolerance
This is a disorder that can last a lifetime. However, if it appears at an early age, it can lead to an insufficiency of calcium and vitamin D. It appears in the form of abdominal swelling, diarrhea, and gas after the ingestion of dairy products. In most cases, in children, removing lactose completely isn’t necessary. However, it’s important to restrict its intake and make certain changes in the child’s diet.
Serious digestive illnesses in children
Appendicitis
This is an inflammation of the appendix caused by an infection. It’s usually quite painful, so it’s usually easy to detect it in time before the gland bursts, causing perforation or peritonitis. The solution is to perform an emergency appendectomy to remove it. Recovery time in children isn’t very long and the operation isn’t very traumatic because it’s not a vital organ.
Hirschsprung’s disease
This disease affects the colon of children between 1 and 3 years of age. It manifests itself with severe constipation that makes it difficult for them to empty their large intestine. Occasionally, it can be complicated by enterocolitis and involve vomiting. Generally, it requires surgery but, in most cases, the cure is total.
Crohn’s disease, one of the most important diseases of the digestive system in children
Crohn’s disease is a chronic disease that mainly affects the small intestine. It causes inflammation and sores that can sometimes extend to the large intestine or affect the entire digestive system. The causes are unknown, but it seems to be related to an affectation of the immune system, so that, for seasons, the patients suffer from flare-ups.
Digestive illnesses in children can affect any organ that makes up the digestive system. The food we eat must undergo a transformation process before becoming molecules that the cells can use. These changes begin in the mouth with chewing and continue in the esophagus and the stomach, where gastric juices break foods down into smaller particles.
The small intestine, specifically the intestinal villi, is the organ of the digestive system where the absorption of nutrients takes place. Finally, digestion ends in the large intestine and the anus with the elimination of those products that we discard.
Other glands such as the pancreas and the gallbladder or organs such as the liver also participate in this process by producing juices that help in the transformation of nutrients. Any alteration during the process makes digestion difficult and, in some cases, lead to digestive illnesses in children.
Mild digestive illnesses in children
Herpetic gingivostomatitis
Herpes simplex virus is a contagious disease caused by infection with herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1). In fact, that’s its primary manifestation. When it comes to adults, it appears in the form of typical herpes in the lip area. However, in children, it causes very painful ulcerous lesions inside the mouth and on the surface of the tongue.

Reflux in newborns
Gastroesophageal reflux occurs when some of the stomach contents back up into the esophagus if the esophageal sphincter doesn’t close properly. In infants, this continued reflux accompanied by vomiting can cause irritation of the area, weight loss, and, on rare occasions, breathing problems.
Infectious gastroenteritis
This contagious disease is caused by eating contaminated food or sucking on an item of an ill child. It’s a very common illness in daycare centers that involves abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, nausea, and fever. It’s usually caused by a 24-hour transient virus (rotavirus).
Moderate digestive illnesses in children
Celiac disease
Celiac disease is a digestive disorder with a marked genetic component that affects the intestinal villi of the small intestine produced by the intake of gluten. In the most extreme cases, children may suffer from severe malnutrition, reflected by growth retardation, rickets, and even mood swings. As for treatment, it involves removing gluten completely from the child’s diet.
Lactose intolerance
This is a disorder that can last a lifetime. However, if it appears at an early age, it can lead to an insufficiency of calcium and vitamin D. It appears in the form of abdominal swelling, diarrhea, and gas after the ingestion of dairy products. In most cases, in children, removing lactose completely isn’t necessary. However, it’s important to restrict its intake and make certain changes in the child’s diet.
Serious digestive illnesses in children
Appendicitis
This is an inflammation of the appendix caused by an infection. It’s usually quite painful, so it’s usually easy to detect it in time before the gland bursts, causing perforation or peritonitis. The solution is to perform an emergency appendectomy to remove it. Recovery time in children isn’t very long and the operation isn’t very traumatic because it’s not a vital organ.

Hirschsprung’s disease
This disease affects the colon of children between 1 and 3 years of age. It manifests itself with severe constipation that makes it difficult for them to empty their large intestine. Occasionally, it can be complicated by enterocolitis and involve vomiting. Generally, it requires surgery but, in most cases, the cure is total.
Crohn’s disease, one of the most important diseases of the digestive system in children
Crohn’s disease is a chronic disease that mainly affects the small intestine. It causes inflammation and sores that can sometimes extend to the large intestine or affect the entire digestive system. The causes are unknown, but it seems to be related to an affectation of the immune system, so that, for seasons, the patients suffer from flare-ups.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Medlineplus (última consulta noviembre 2019). Enfermedades del sistema digestivo [artículo en web]. Recuperado de: www.medlineplus.org
- Medlineplus (última consulta noviembre 2019). Reflujo gastroesofágico [artículo en web]. Recuperado de: www.medlineplus.org
- Marquez, C. (última consulta noviembre 2019). Qué es la gingivioestomatitis y que la causa [articulo en web]. Recuperado de: www.hospitalcruzrojacordoba.es
- Standford Childre’s Health (última consulta noviembre 2019). Apendicitis en niños [artículo en web]. Recuperado de: www. standfordchildren.org
- Standford Childre’s Health (última consulta noviembre 2019). Enfermedad de Crohn[artículo en web]. Recuperado de: www. standfordchildren.org
- NIH (última consulta nogiembre 2019). Intolerancia a la lactosa [artículo en web]. Recuperado de: www.niddk.nih.gov
- Denham, J. (julio 2018). Enfermedad de Hirschsprung [artículo en web]. Recuperado de: www.kidshealth.org
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








